| |

TRIGONOMETRY
Trigonometry (from Greek trigōnon "triangle" + metron "measure") is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between the sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves. The field evolved during the third century B.C. as a branch of geometry used extensively for astronomical studies.
Trigonometry is usually taught in middle and secondary schools either as a separate course or as part of a precalculus curriculum. It has applications in both pure mathematics and applied mathematics, where it is essential in many branches of science and technology. A branch of trigonometry, called spherical trigonometry, studies triangles on spheres, and is important in astronomy and navigation.
Table of Trigonometric Identities
Reciprocal identities
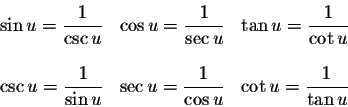
Pythagorean Identities

Quotient Identities
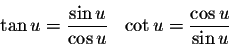
Co-Function Identities
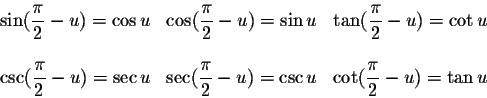
Even-Odd Identities

Sum-Difference Formulas
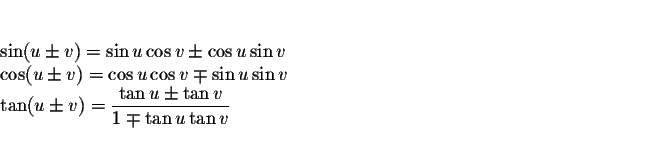
Double Angle Formulas
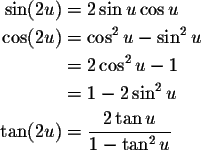
Power-Reducing/Half Angle Formulas
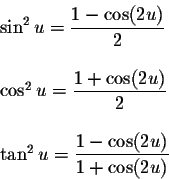
Sum-to-Product Formulas

Product-to-Sum Formulas
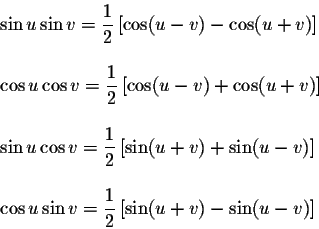
TUTORIALS:
|
|
 |

|
is an engineering discipline which uses the scientific knowledge of the behavior and effects of electrons to develop components, devices, systems, or equipment (as in electron tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, and printed circuit boards) that uses electricity as part of its driving force. Both terms denote a broad engineering field that encompasses many sub fields including those that deal with power, instrumentation engineering, telecommunications, semiconductor circuit design, and many others.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_engineering |
|
|
 |
 |
|

